

Do you sometimes feel a bit lost when deciding which tense to use? Are you a little unsure of the differences between the present tenses? Does jumping to and fro between tenses leave you confused? If you’ve answered ‘yes’ to any of these, then you’ll be happy to know we’ve created a grammar guide for you: Understanding Present Simple and Present Perfect.
These two tenses have similar names, and they refer to periods of time which are, in a way, similar. However, there are clear differences, and making mistakes when using them can lead to a breakdown in communication, or even worse, an angry teacher! Mastering grammar tenses is important!
Firstly, don’t worry if you’re not a grammar expert. We’ll avoid using a lot of jargon and instead, we’ll go through the grammar using basic terms. On the other hand, you might be someone who feels very confident using grammar and just wants to brush up on it. We all need to review things from time to time! With that in mind, let’s get to work on tense usage in English.
The Present Simple – 3 usages
We use the Present Simple to describe actions or situations that are routines, habits, general facts, states of being and permanent situations. In short, we use it to talk about things we like, things we do and things we have.
1. Routines and habits
We use the Present Simple to describe actions that happen regularly (or don’t happen regularly) or as part of a routine.
I watch my football team every weekend, and they usually let me down!
She usually rides her bike to work. That’s why she’s so fit!
We always play games in class, because we always work hard first!
2. General facts and states of being
We use the Present Simple to talk about general facts and states that are true in the present.
The Earth orbits the sun.
Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.
Seville is scorching at this time of year.
3. Permanent situations
We also use the Present Simple to refer to permanent or long-lasting situations or conditions.
My aunt lives in Chicago.
He works as an artist.
She is really into parkour.
How do we make the Present Simple?
The verb takes the base form (the infinitive without ‘to’), and as you can see from the examples, we add an ‘s’ with the third person singular (he, she, it). However, there are some spelling exceptions:
When the verb ends in -ch, -ss, -sh, -x or -zz, we add -es.
She watches too much TV.
When the verb ends in a consonant + -y we change y to i and add -es.
Harry studies grammar every night.
Have, go, do and be are irregular.
Laura has an older brother.
Check out these examples of the Present Simple in this TV series compilation. Can you match each example to the usage?
The Present Perfect – 3 usages
We use the Present Perfect to describe actions or events that started in the past, but are related to the present moment.
1. Recently completed actions
We use the Present Perfect tense when an event or action happened at some point in the past, is relevant to or has an impact on the present.
I have just finished this book. What a page-turner!
She has lost her mobile phone again! How can we call her?
2. Ongoing actions with a connection to the present
We also use the Present Perfect to talk about actions or events that started in the past and are still happening in the present.
Son Heung-Min has played for the Spurs since 2015.
I have lived in this town all my life. I know it like the back of my hand.
3. Actions with unspecified times
We can also use the Present Perfect when the time of the action is not specified or not important. This puts emphasis on the fact that the action has been completed.
She has been to Mexico five times.
I have seen all of the James Bond films.
How do we make the Present Perfect?
We use the subject, followed by the auxiliary verb ‘have’ or ‘has’, and then the past participle of the main verb. Irregular verbs have unique past participle forms, and we can find these in the third column of the irregular verb table. However, we make regular past participle verbs by adding ‘-ed’.
How about these examples of the Present Perfect in TV clips? Can you match them to the usage?
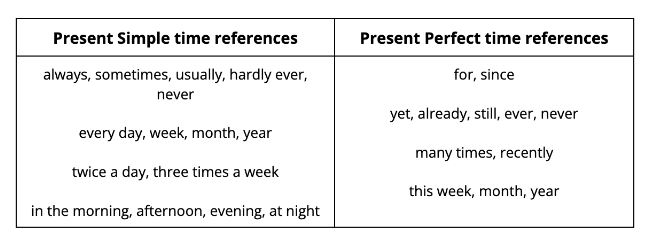
Are there any useful words to help us?
We use each tense to refer to different time periods. Luckily, there are useful time references which help us know which tense to use. It’s a good idea to make a note of these!
Look at the change in meaning
Often, it’s useful to compare two sentences so you can really understand the difference. Can you match the examples to the uses mentioned earlier in the blog?
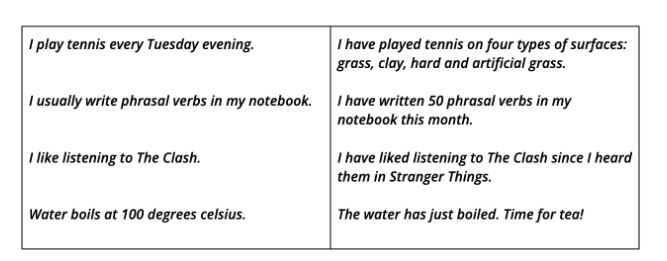
As always, the best way to remember new grammar is to write your own personal sentences. Try replacing the key words in our examples with something connected to your life!
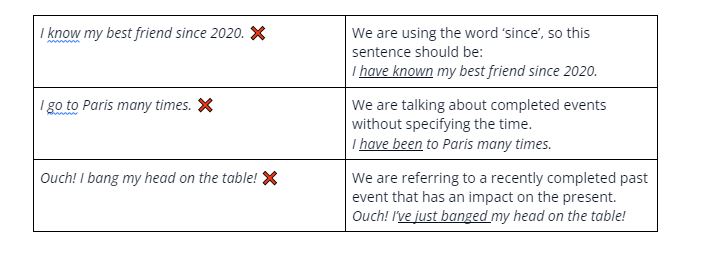
Common errors in use
Be careful when using these grammar tenses. Here are some typical mistakes that we’ve corrected for you.
Remember that English grammar is not exactly the same as the grammar in your language. Therefore, it is not always a good idea to make direct translations. It’s better to fully immerse yourself in English grammar. Keep reading for some tips to help you consolidate your understanding.
How to choose the correct tense
- Look carefully for examples of time references.
- Try the sentence in both tenses and try to figure out which usage is needed.
- Think about how the choice of tense can affect the meaning of a sentence.
- Read in English and look for examples. Highlight them and identify the usage.
Final thoughts
- The Present Simple and Present Perfect are alike in name, but very different in usage.
- Present Simple = routines, habits, general facts and permanent situations.
- Present Perfect = recently completed actions, actions with an impact on the present and completed actions with an unspecified time.
- A sound understanding of these two tenses will lead to clear communication.
- Practice makes perfect!
Don’t stop yet! Check out these blogs for more useful tips:
4 Conditionals In English And When To Use Them
4 Future Tenses In English And How To Use Them
Stop Making These 7 Grammar Mistakes
And remember, learning is always more enjoyable with other people! Find the class to suit your needs!
Glossary for Language Learners
Find the following words in the article and then write down any new ones you didn’t know.
To and fro (adv): very busy with something.
Jargon (n): speak angrily at someone because they’ve done something wrong.
Brush up on (pv): make people who have not met before feel more relaxed.
Let someone down (pv): the last part of a joke, the funny part!
Scorching (adj): be different to something.
Be really into something (exp): in this context, to ‘get’ a joke, means to understand a joke.
Page-turner (n): the place where very young children go when their parents are at work.
To know something like the back of your hand (exp): change the colour of something, usually hair.
Figure out (pv): a set of clothes which you wear to look like something or someone.
Alike (adj): find the origin of something.
Sound (adj): prevent someone or something from harming you.
Key
adv = adverb
n = noun
pv = phrasal verb
adj = adjective
exp = expression
Halloween Humour: Jokes, Puns and Riddles
- By: oxfordadmin
3 Easy Ways To Use Music To Improve Your English
- By: oxfordadmin
Related Post
-

In, On and At: Dealing with Tr
Does this situation sound familiar? You’re writing a message to a friend in English arranging to meet. As you start to... Read More
- Blog
-
24/07/2024
-

A Guide to English for Tech Pr
If you work in the tech industry, chances are you’re learning English to advance your career. After all, it’s the mo... Read More
- Blog
-
16/07/2024
-

What Is The Schwa Sound (And W
If you’ve never heard of the schwa before, you might think it’s an unusual piece of pronunciation. It’s actually t... Read More
- Blog
-
12/06/2024
-

A Guide to English Accents Aro
Countries can have extremely different English accents despite sharing the same language. Just take the word ‘water’... Read More
- Blog
-
07/05/2024
-

Passing Cambridge C2 Proficien
Many sections of the Cambridge Proficiency are multiple-choice, so Part 2 of the Reading and Use of English can seem cha... Read More
- Blog
-
24/04/2024
-

Exploring the Impact of AI in
Gone are the days of learning from phrasebooks and filling in worksheets for homework. Now students have access to a wid... Read More
- Blog
-
10/04/2024
-

Everything You Need To Know Ab
Although you learn plural nouns early on, they can be challenging. There are many rules and exceptions to remember plus ... Read More
- Blog
-
28/02/2024
-

The Importance of English For
No matter where you live, you’ve probably experienced record-breaking temperatures and severe weather. You may have se... Read More
- Blog
-
16/02/2024
-

Discovering Barcelona Through
We all know that Barcelona is a fantastic city to live in. You only need to spend the afternoon wandering around one of ... Read More
- Blog
-
24/01/2024
-

8 New Words To Improve Your Vo
The arrival of a new year presents an ideal opportunity to work on your language goals. Whether you’re preparing for a... Read More
- Blog
-
10/01/2024
-

Learning English through Chris
It’s beginning to look a lot like Christmas! If you resisted the urge to sing that line instead of saying it, then, we... Read More
- Blog
-
19/12/2023
-

24 Christmas Phrases for Joyfu
‘Tis the season to be jolly, and what better way to get ready for the festive period than by learning some typical Chr... Read More
- Blog
-
13/12/2023
-

3 Easy Ways To Use Music To Im
Are you ready to embark on your latest journey towards mastering the English language? We all know that music is there f... Read More
- Blog
-
21/11/2023
-

Halloween Humour: Jokes, Puns
We all need a break from time to time. Sometimes we’re up to our eyeballs in projects at work, and we just need a mome... Read More
- Blog
-
30/10/2023
-

English for Business: 7 Ways L
If you’re interested in getting a promotion at work, earning a higher salary or landing your dream job, then working o... Read More
- Blog
-
18/10/2023
-

A Beginner’s Guide to Ch
Understanding the need for exams An official exam is a fantastic way to demonstrate your English. Why? Firstly,... Read More
- Blog
-
04/10/2023
-

English Tongue Twisters to Imp
One of the most fun ways to practise and improve your pronunciation is with tongue twisters. That’s because they’re ... Read More
- Blog
-
23/08/2023
-

25 years of Oxford House – O
We all know that fantastic feeling we have after completing an academic year: nine months of English classes, often twic... Read More
- Blog
-
09/08/2023
-

Guide to the Cambridge C2 Prof
Are you working towards the Cambridge C2 Proficiency (CPE) exam? Have you been having sleepless nights thinking about wh... Read More
- Blog
-
02/08/2023
-

9 Tips For Communicating With
When travelling to or living in an English-speaking country, getting to know the local people can greatly enhance your e... Read More
- Blog
-
21/06/2023
-

Guide to the Cambridge C2 Prof
Are you preparing for the Cambridge C2 Proficiency (CPE) writing exam? If those pre-exam jitters have started to appear,... Read More
- Blog
-
31/05/2023
-

English Vocabulary For Getting
Are you feeling bored of the way your hair looks? Perhaps it’s time for a new you. All you need to do is make an appoi... Read More
- Blog
-
17/05/2023
-

5 Spelling Rules For Comparati
Messi or Ronaldo? Pizza or sushi? Going to the cinema or bingeing on a series at home? A beach holiday or a walking trip... Read More
- Blog
-
03/05/2023
-

Guide to the Cambridge C2 Prof
Are you preparing for the Cambridge C2 Proficiency (CPE) writing exam? If so, you may be feeling a little nervous and co... Read More
- Blog
-
19/04/2023
-

Improve your English pronuncia
What are some of the trickiest words to pronounce in English? Well, we’ve compiled a useful list of ten of the most di... Read More
- Blog
-
05/04/2023
-

Using Language Reactor To Lear
If you love watching Netflix series and videos on YouTube to learn English, then you need to download the Language React... Read More
- Blog
-
22/03/2023
-

Guide to the Cambridge C2 Prof
Are you preparing for the Cambridge C2 Proficiency (CPE) exam? Would you like to know some tips to help you feel more at... Read More
- Blog
-
08/03/2023
-

How to use ChatGPT to practise
Are you on the lookout for an extra way to practise your English? Do you wish you had an expert available at 2 a.m. that... Read More
- Blog
-
22/02/2023
-

Guide to the Cambridge C2 Prof
Well done. You’ve been moving along your English language journey for some time now. You remember the days of telling ... Read More
- Blog
-
08/02/2023
-

Tips for the IELTS listening s
Are you preparing for the IELTS exam and need some help with the listening section? If so, then you’ll know that the l... Read More
- Blog
-
17/01/2023
-

7 new English words to improve
A new year is a perfect opportunity to focus on your language goals. Maybe you are working towards an official exam. Per... Read More
- Blog
-
04/01/2023
-

How to Write a C1 Advanced Ema
Did you know that there are two parts to the C1 Advanced Writing exam? Part 1 is always a mandatory . Part 2 has ... Read More
- Blog
-
21/12/2022
-

5 Interesting Christmas tradit
When you think of the word Christmas, what springs to mind? For most people, it will be words like home, family and trad... Read More
- Blog
-
07/12/2022
-

How to write a C1 Advanced Rep
Are you preparing for the Cambridge C1 Advanced exam and need a hand with writing your report/proposal for Part 2 of the... Read More
- Blog
-
16/11/2022
-

5 of the best apps to improve
Would you like to improve your English listening skills? With all the technology that we have at our fingertips nowadays... Read More
- Blog
-
02/11/2022
-

Tips for the IELTS Reading sec
Looking for some tips to get a high band score in the IELTS Academic Reading exam? If so, then you’re in the right pla... Read More
- Blog
-
19/10/2022
-

The 5 best Halloween movies to
Boo! Are you a fan of Halloween? It’s that scary time of year again when the creepy creatures come out to play, and th... Read More
- Blog
-
12/10/2022
-

How to Write a Review for Camb
Are you planning to take the Cambridge C1 Advanced (CAE) exam? If so, you will need to complete two pieces of writin... Read More
- Blog
-
28/09/2022
-

How To Use Relative Pronouns i
Today we’re taking a look at some English grammar that sometimes trips up language learners. In fact, we’ve just use... Read More
- Blog
-
14/09/2022
-

How To Get Top Marks: Cambridg
So you’re taking the ? If so, you’ll know that you have four sections to prepare for: speaking, reading and use of E... Read More
- Blog
-
24/08/2022
-

Travel Vocabulary To Get Your
Summer is here and we can’t wait to go on our summer holidays! If you’re thinking about travelling overseas this yea... Read More
- Blog
-
10/08/2022
-

How To Get A High Score In The
So you’re preparing for the ! From wanting to live and work abroad to going to university in an English-speaking count... Read More
- Blog
-
27/07/2022
-

10 English Idioms To Take To T
Is there anything better than cooling off in the sea on a hot summer’s day? Well, if you live in Barcelona you hav... Read More
- Blog
-
06/07/2022
-

Tips for IELTS speaking sectio
Are you preparing for the IELTS test? If so, you’ll need to do the speaking section. While many people find speaking t... Read More
- Blog
-
15/06/2022
-

How to use 6 different English
Just when you think English couldn’t get any more confusing, we introduce you to English pronouns! The reason why peop... Read More
- Blog
-
01/06/2022
-

How to get top marks: B2 First
Congratulations – you’ve made it to the B2 First Reading and Use of English Part 7! Yet, before we get too excited, ... Read More
- Blog
-
18/05/2022
-

5 Of The Best Apps For Improvi
Speaking is often thought to be the hardest skill to master when learning English. What’s more, there are hundreds of ... Read More
- Blog
-
04/05/2022
-

How to get top marks: B2 First
Do you like putting together puzzles? If so, your problem solving skills can actually help you with B2 First Reading and... Read More
- Blog
-
20/04/2022
-

8 Vocabulary Mistakes Spanish
If you ask a Spanish speaker what they find difficult about English language learning, they may mention false friends an... Read More
- Blog
-
06/04/2022
-

How To Get Top Marks: B2 First
Picture this: You’re in your B2 First exam and you’ve finished the Use of English part. You can put it behind you fo... Read More
- Blog
-
16/03/2022
-

12 Business Phrasal Verbs to K
Want to improve your English for professional reasons? You’re in the right place. When working in English, it’s comm... Read More
- Blog
-
02/03/2022
-

How to use articles (a, an, th
Knowing what articles are and when to use them in English can be difficult for language learners to pick up. Especially ... Read More
- Blog
-
15/02/2022
-

How to get top marks: B2 First
Are you preparing for ? Reading and Use of English Part 4 may not be your cup of tea – in fact most students feel quit... Read More
- Blog
-
02/02/2022
-

Passing B2 First Part 3: Readi
Are you studying for the B2 First exam? You’re in the right place! In this series of blogs we want to show you al... Read More
- Blog
-
19/01/2022
-

8 new English words you need f
New words spring up each year! They often come from popular culture, social and political issues, and innovations in tec... Read More
- Blog
-
05/01/2022
-

7 of the Best Apps for Learnin
If you find yourself commuting often and spending a lot of time on the bus, you’ll most likely turn towards playing ga... Read More
- Blog
-
15/12/2021
-

How To Get Top Marks: B2 First
The B2 First is one of the most popular English exams for students of English. It is a recognised qualification that can... Read More
- Blog
-
01/12/2021
-

4 Different Types Of Modal Ver
What are modal verbs? They are not quite the same as regular verbs such as play, walk and swim. Modal verbs are a type o... Read More
- Blog
-
24/11/2021
-

How To Get Top Marks: B2 First
So you’ve decided to take the ! Formerly known as FCE or the First Certificate, this is by far most popular exam. Whe... Read More
- Blog
-
10/11/2021
-

Useful Expressions For Negotia
A lot of our global business is conducted in English. So, there’s a strong chance you may have to learn how to negotia... Read More
- Blog
-
20/10/2021
-

Passing C1 Advanced Part 8: Re
If you’re wondering how to do Part 8 of the Reading and Use of English paper, you’re in the right place! After s... Read More
- Blog
-
06/10/2021
-

The Difference Between IELTS G
You’ve probably heard of . It’s the world’s leading test for study, work and migration after all. And as the world... Read More
- Blog
-
22/09/2021
-

Passing C1 Advanced Part 7: Re
Welcome to Part 7 of the Reading and Use of English paper. This task is a bit like a jigsaw puzzle. One where you have ... Read More
- Blog
-
15/09/2021
-

The Benefits Of Learning Engli
Who said learning English was just for the young? You're never too old to learn something new. There are plenty of benef... Read More
- Blog
-
25/08/2021
-

How To Get A High Score In The
So, you’re preparing to take the . You’ve been studying for each of the four sections; reading, writing, speaking an... Read More
- Blog
-
11/08/2021
-

6 Reels Accounts to Learn Engl
Are you looking for ways to learn English during the summer holidays? We’ve got you covered – Instagram Reels is a n... Read More
- Blog
-
21/07/2021
-

Passing Cambridge C1 Advanced
Well done you! You’ve made it to Part 6 of the Reading and Use of English exam. Not long to go now – just three mor... Read More
- Blog
-
07/07/2021
-

8 Resources To Help Beginner E
Learning a new language is hard, but fun. If you are learning English but need some help, our monthly course is what y... Read More
- Blog
-
23/06/2021
-

5 Famous Speeches To Help you
Everyone likes listening to inspiring speeches. Gifted speakers have a way of making people want to listen and take acti... Read More
- Blog
-
16/06/2021
-

How To Write A B2 First Formal
Dear reader… We sincerely hope you enjoyed our previous blog posts about the Writing section of the B2 First. As promi... Read More
- Blog
-
01/06/2021
-

4 Conditionals In English And
Conditionals? Is that something you use after shampooing your hair? Not quite. You may have heard your English teacher t... Read More
- Blog
-
19/05/2021
-

Passing Cambridge C1 Advanced
After racing through the first four parts of the Cambridge English Reading and Use of English paper, you’ve managed t... Read More
- Blog
-
05/05/2021
-
7 Of The Best Apps For Learnin
There are roughly 170,000 words in use in the English language. Thankfully, most native English speakers only have a voc... Read More
- Blog
-
21/04/2021
-

How to write a B2 First inform
You're probably very familiar with sending emails (and sometimes letters) in your first language. But how about in Engli... Read More
- Blog
-
07/04/2021
-

How can I teach my kids Englis
Keep kids’ minds sharp over the Easter holidays with some entertaining, educational activities in English. There are l... Read More
- Blog
-
29/03/2021
-

How Roxana went from Beginner
Roxana Milanes is twenty five and from Cuba. She began English classes back in May 2019 at Oxford House, and since then ... Read More
- Blog
-
24/03/2021
-

4 Future Tenses In English And
“Your future is whatever you make it, so make it a good one.” - Doc Brown, Back to the future. Just like the and... Read More
- Blog
-
10/03/2021
-

10 Business Idioms For The Wor
Business idioms are used throughout the workplace. In meetings, conversations and even whilst making at the coffee mac... Read More
- Blog
-
17/02/2021
-
5 Tips For Reading The News In
We spend hours consuming the news. With one click of a button we have access to thousands of news stories all on our pho... Read More
- Blog
-
03/02/2021
-

How To Write a Report: Cambrid
Imagine the scene. It’s exam day. You’re nearly at the end of your . You’ve just finished writing Part 1 - , and n... Read More
- Blog
-
20/01/2021
-

8 English Words You Need For 2
Back in December 2019, we sat down and attempted to make a list of . No one could have predicted the year that was about... Read More
- Blog
-
07/01/2021
-

5 Christmas Movies On Netflix
Christmas movies are one of the best things about the holiday season. They’re fun, they get you in the mood for the ho... Read More
- Blog
-
16/12/2020
-

MigraCode: An Inspiring New Pa
Oxford House are extremely proud to announce our partnership with MigraCode - a Barcelona-based charity which trains ref... Read More
- Blog
-
02/12/2020
-

The Ultimate Guide To Video Co
The age of telecommunication is well and truly here. Most of our business meetings now take place via video conferencing... Read More
- Blog
-
24/11/2020
-

6 Pronunciation Mistakes Spani
One of the biggest challenges for Spanish speakers when learning English is pronunciation. Often it’s a struggle to pr... Read More
- Blog
-
11/11/2020
-

6 Ways You Can Learn English w
“Alexa, what exactly are you?” Alexa is a virtual AI assistant owned by Amazon. She is voice-activated - like Sir... Read More
- Blog
-
03/11/2020
-

Passing Cambridge C1 Advanced:
Okay, take a deep breath. We’re about to enter the danger zone of the Cambridge exam - Reading and Use of English Par... Read More
- Blog
-
19/10/2020
-

What’s new at Oxford House f
Welcome to the new school year! It’s great to have you back. We’d like to remind you that , and classes are all st... Read More
- Blog
-
05/10/2020
-
European Languages Day: Where
The 26th of September is . It’s a day to celebrate Europe’s rich linguistic diversity and show the importance of lan... Read More
- Blog
-
24/09/2020
-

Back To School: 9 Tips For Lan
It’s the start of a new academic term and new courses are about to begin. This is the perfect opportunity to set your ... Read More
- Blog
-
09/09/2020
-

How to Maximise Your Online Co
If there’s one good thing to come out of this year, it’s that learning a language has never been so easy or accessib... Read More
- Blog
-
20/08/2020
-

How To Learn English With TikT
Are you bored of Facebook? Tired of Instagram? Don’t feel part of the Twitter generation? Perhaps what you’re lookin... Read More
- Blog
-
06/08/2020
-
A Brief Guide To Different Bri
It’s a fact! The UK is obsessed with the way people talk. And with , it’s no surprise why. That’s right, accents a... Read More
- Blog
-
20/07/2020
-

Study English This Summer At O
Summer is here! And more than ever, we’re in need of a bit of sunshine. But with travel restrictions still in place, m... Read More
- Blog
-
02/07/2020
-

5 Reasons To Learn English Out
As Barcelona and the rest of Spain enters the ‘new normality’, it’s time to plan ahead for the summer. Kids and te... Read More
- Blog
-
25/06/2020
-

5 Free Online Resources For Ca
Are you preparing for a Cambridge English qualification? Have you devoured all of your past papers and need some extra e... Read More
- Blog
-
09/06/2020
-

6 Different Uses Of The Word �
The word ‘get’ is one of the most common and versatile verbs in English. It can be used in lots of different ways, a... Read More
- Blog
-
27/05/2020
-

What Are The 4 Present Tenses
There are three main verb tenses in English - , the present and the future - which each have various forms and uses. Tod... Read More
- Blog
-
13/05/2020
-

5 Of The Best Netflix Series T
On average, Netflix subscribers spend streaming their favourite content. With so many binge-worthy series out there, it... Read More
- Blog
-
29/04/2020
-

Continue Studying Online At Ox
Due to the ongoing emergency lockdown measures imposed by the Spanish Government . We don’t know when we will be a... Read More
- Blog
-
22/04/2020
-

Five Ways To celebrate Sant Jo
The feast of Sant Jordi is one of Barcelona’s most popular and enduring celebrations. Sant Jordi is the patron saint o... Read More
- Blog
-
21/04/2020
-

What’s It Like To Study Onli
Educational institutions all over the world have shut their doors. From nurseries to universities, business schools to l... Read More
- Blog
-
15/04/2020
-

6 Benefits of Learning English
Whatever your new year’s resolution was this year, it probably didn’t involve staying at home all day. For many of u... Read More
- Blog
-
03/04/2020
-

9 Tips For Studying A Language
With the recent outbreak of Covid-19, many of us may have to gather our books and study from home. Schools are clos... Read More
- Blog
-
25/03/2020
-

10 Ways To Learn English At Ho
Being stuck inside can make you feel like you’re going crazy. But why not use this time to your advantage, and work on... Read More
- Blog
-
18/03/2020
-

Important Information –
Dear students, Due to the recent emergency measures from the Government concerning COVID-19, Oxford House premises wi... Read More
- Blog
-
13/03/2020
-

7 Books You Should Read To Imp
Reading is one of the best ways to practice English. It’s fun, relaxing and helps you improve your comprehension skill... Read More
- Blog
-
11/03/2020
-

Your Guide To Moving To The US
So that’s it! It’s decided, you’re moving to the USA. It’s time to hike the soaring mountains, listen to country... Read More
- Blog
-
04/03/2020
-

How to write a C1 Advanced Ess
The is an excellent qualification to aim for if you’re thinking of studying or working abroad. It’s recognised by u... Read More
- Blog
-
26/02/2020
-

Small Talk For Business Englis
Like it or not, small talk is an important part of business. Whether it’s in a lift, at a conference, in a meeting roo... Read More
- Blog
-
19/02/2020
-

English Vocabulary For Going O
It’s time for that famous celebration of love and romance - Valentine’s Day! It is inspired by the sad story of Sain... Read More
- Blog
-
12/02/2020
-

IELTS: Writing Part 2 –
When it comes to exams, preparation is the key to success - and the IELTS Writing Paper Part 2 is no exception! It is wo... Read More
- Blog
-
05/02/2020
-

5 Unmissable Events at Oxford
At Oxford House, we know learning a language extends beyond the classroom. It’s important to practise your skills in m... Read More
- Blog
-
29/01/2020
-

Am I ready for the C1 Advanced
Congratulations! You’ve passed your Cambridge B2 First exam. It was a hard road but you did it. Now what’s next? Som... Read More
- Blog
-
21/01/2020
-

Everything You Need To Know Ab
Ireland is known as the Emerald Isle. When you see its lush green landscape and breathtaking views, it’s easy to see w... Read More
- Blog
-
15/01/2020
-

How SMART Goals Can Help You I
New year, new you. As one year ends and another begins, many of us like to set ourselves goals in order to make our live... Read More
- Blog
-
09/01/2020
-

15 New English Words You Need
Each year new words enter the English language. Some are added to dictionaries like . Others are old words that are give... Read More
- Blog
-
07/01/2020
-

Our Year In Review: Top 10 Blo
2019 went by in a flash - and what a year it’s been! We’re just as excited to be looking back on the past 12 months ... Read More
- Blog
-
23/12/2019
-

Telephone Interviews In Englis
Telephone interviews in English can seem scary. Employers often use them to filter-out candidates before the face-to-fa... Read More
- Blog
-
19/12/2019
-

How to Write a Great Article i
Writing in your only language can be a challenge, but writing in another language can be a complete nightmare ! Where do... Read More
- Blog
-
11/12/2019
-

A Black Friday Guide to Shoppi
Black Friday is the day after Thanksgiving. Traditionally, it signals the start of the Christmas shopping period. Expect... Read More
- Blog
-
26/11/2019
-

Passing C1 Advanced: Part 3 Re
The (CAE) is a high-level qualification, designed to show that candidates are confident and flexible language users who... Read More
- Blog
-
25/11/2019
-

AI Translators: The Future Of
Many people believe that artificial intelligence (AI) translators are surpassing human translators in their ability to a... Read More
- Blog
-
13/11/2019
-

8 Of The Best Apps For Learnin
Apps are a great tool for learning English. They are quick, easy to access and fun. It’s almost like having a mini cla... Read More
- Blog
-
07/11/2019
-

6 Ways To Improve Your Speakin
There are four linguistic skills that you utilise when learning a new language: reading, writing speaking and listening.... Read More
- Blog
-
31/10/2019
-

Passing Cambridge C2 Proficien
So, you’ve moved onto Part 3, and after completing Part 2 it’s probably a welcome relief to be given some help with ... Read More
- Blog
-
23/10/2019
-

8 Resources To Build Your Busi
Whether it’s in meetings, telephone conversations or networking events, you’ll find specific vocabulary and buzzword... Read More
- Blog
-
17/10/2019
-

5 Ways to Become a Better Lear
It’s time for some back-to-school motivation. The new school year is about to start and everyone is feeling refreshed ... Read More
- Blog
-
18/09/2019
-

Our 10 Favourite YouTubers To
Haven’t you heard? Nobody is watching the TV anymore - 2019 is the year of the YouTuber! If you’re an English langu... Read More
- Blog
-
04/09/2019
-

Passing Cambridge C1 Advanced:
So, you’ve completed the of your Cambridge C1 Advanced (CAE). Now it’s time to sit back and enjoy the rest of the e... Read More
- Blog
-
28/08/2019
-

The Secret French Words Hidden
“The problem with the French is that they have no word for entrepreneur.” This phrase was attributed to George W. B... Read More
- Blog
-
22/08/2019
-

The Ultimate Guide To Gràcia
The Gràcia Festival, or , is an annual celebration taking place in the lovely, bohemian neighbourhood of Gràcia in upt... Read More
- Blog
-
15/08/2019
-

5 Things To Do In Barcelona In
Barcelona residents will often tell you than nothing happens in August. It’s too hot and everyone escapes to little vi... Read More
- Blog
-
07/08/2019
-

4 Past Tenses and When to Use
Do you have difficulty with the past tenses in English? Do you know the difference between the past simple and past perf... Read More
- Blog
-
31/07/2019
-

How To Write A Review: Cambrid
Students who are taking their B2 First Certificate exam (FCE) will be asked to do two pieces of writing within an 80 min... Read More
- Blog
-
24/07/2019
-

8 Hidden Benefits of Being Bil
Unless you were raised to be bilingual, speaking two languages can require years of study and hard work. Even once you�... Read More
- Blog
-
17/07/2019
-

7 Films to Practise Your Engli
What’s better than watching a fantastic, original-language movie in a theatre? Watching a fantastic, original-language... Read More
- Blog
-
03/07/2019
-
The 10 Best Instagram Accounts
Ever wonder how much time you spend on your phone a day? According to the latest studies, the average person spends on ... Read More
- Blog
-
26/06/2019
-

Challenge Yourself This Summer
Here comes the sun! That’s right, summer is on its way and, for many, that means a chance to take a well-deserved brea... Read More
- Blog
-
19/06/2019
-

Passing Cambridge C1 Advanced
You’ve done the hard part and finally registered for your , congratulations! Now all you need to do is pass it! H... Read More
- Blog
-
05/06/2019
-

These 5 Soft Skills Will Boost
Everyone is talking about soft skills. They are the personal traits that allow you to be mentally elastic, to adapt to n... Read More
- Blog
-
29/05/2019
-

Which English Exam Is Right Fo
Are you struggling to decide which English language exam to take? You’re not alone: with so many different options on ... Read More
- Blog
-
23/05/2019
-

Passing C2 Proficiency: A Guid
We’re sure you’ve done a great job answering the questions for of your . But now you’re faced with a completely d... Read More
- Blog
-
15/05/2019
-

Sant Jordi – Dragons, Bo
Imagine you have woken up in Barcelona for the first time in your life. You walk outside and you notice something unusua... Read More
- Blog
-
23/04/2019
-

5 Ways To Improve Your Listeni
Have you ever put on an English radio station or podcast and gone to sleep, hoping that when you wake up in the morning ... Read More
- Blog
-
10/04/2019
-

The Simple Guide To Communicat
What’s the most challenging thing about going on holiday in an English speaking country? Twenty years ago you might ha... Read More
- Blog
-
03/04/2019
-

Stop Making These 7 Grammar Mi
No matter how long you've been learning a language, you're likely to make a mistake every once in a while. The big ones ... Read More
- Blog
-
27/03/2019
-

How To Pass Your First Job Int
Passing a job interview in a language that’s not your mother tongue is always a challenge – but however daunting i... Read More
- Blog
-
20/03/2019
-

5 Ways To Practise Your Speaki
“How many languages do you speak?” This is what we ask when we want to know about someone’s language skills... Read More
- Blog
-
13/03/2019
-

Passing C2 Proficiency: A Guid
You have survived the Use of English section of your , but now you are faced with a long text full of strange language, ... Read More
- Blog
-
06/03/2019
-

Improve Your English Accent Wi
Turn on a radio anywhere in the world and it won’t take long before you’re listening to an English song. And, if you... Read More
- Blog
-
20/02/2019
-

10 English Expressions To Fall
It’s nearly Valentine’s day and love is in the air at Oxford House. We’ll soon be surrounded by heart-shaped ballo... Read More
- Blog
-
13/02/2019
-

7 Graded Readers To Help You P
Graded readers are adaptations of famous stories, or original books aimed at language learners. They are written to help... Read More
- Blog
-
07/02/2019
-

6 Tools To Take Your Writing T
Written language is as important today as it has ever been. Whether you want to prepare for an , to respond to or it’... Read More
- Blog
-
30/01/2019
-

EF Report: Do Spanish Schools
The new year is here and many of us will be making promises about improving our language skills in 2019. However, how ma... Read More
- Blog
-
23/01/2019
-

Our 10 Most Popular Blog Posts
It’s been a whirlwind 2018. We’ve made so many amazing memories - from our twentieth-anniversary party to some enter... Read More
- Blog
-
04/01/2019
-

Time For A Career Change? Here
Have you ever wondered what it would be like to get a job in an international company? Perhaps you’ve thought about tr... Read More
- Blog
-
12/12/2018
-

Eaquals Accreditation: A Big S
We are delighted to be going through the final stages of our accreditation, which will help us provide the best languag... Read More
- Blog
-
21/11/2018
-

A Guide To The Cambridge Engli
Making the decision to do a Cambridge English language qualification can be intimidating. Whether you’re taking it bec... Read More
- Blog
-
14/11/2018
-

8 Top Tips To Get The Most Out
A language exchange (or Intercambio in Spanish) is an excellent way to practise English outside of the classroom. The a... Read More
- Blog
-
07/11/2018
-

The Haunted History And Terrib
The nights are drawing in and the leaves are falling from the trees. As our minds turn to the cold and frosty winter nig... Read More
- Blog
-
31/10/2018
-

Why Oxford House Is More Than
If you’re a student at , you’ll know it is far more than just a language academy. It’s a place to socialise, make ... Read More
- Blog
-
24/10/2018
-

10 Crazy Things You Probably D
From funny bananas, super long words and excitable foxes, our latest infographic explores 10 intriguing facts about the ... Read More
- Blog
-
04/10/2018
-

Meet our Director of Studies &
If you’ve been studying at Oxford House for a while there’s a good chance that you’ll recognise Judy - with her bi... Read More
- Blog
-
25/09/2018
-

Which English Course Is Right
The new school year is about to begin and many of you are probably thinking that it’s about time to take the plunge an... Read More
- Blog
-
19/09/2018
-

5 Ways To Get Over The Holiday
We head off on vacation full of excitement and joy. It’s a time to explore somewhere new, relax and spend time with ou... Read More
- Blog
-
13/09/2018
-

10 Essential Aussie Expression
Learning English is difficult! With its irregular verbs, tricky pronunciation and even harder spelling, lots of students... Read More
- Blog
-
06/09/2018
-

5 Great Apps To Give Your Engl
The next time you’re walking down the street, in a waiting room, or on public transport in Barcelona take a look aroun... Read More
- Blog
-
29/08/2018
-

Here’s Why You Should Move T
Many students have aspirations to move abroad. This might be for a number of reasons such as to find a new job, to impro... Read More
- Blog
-
22/08/2018
-

Improving Your Pronunciation W
What do English, Maori, Vietnamese and Zulu have in common? Along with another , they all use the . If your first la... Read More
- Blog
-
16/08/2018
-

How To Improve Your English Us
Netflix has changed the way we spend our free time. We don’t have to wait a week for a new episode of our favourite TV... Read More
- Blog
-
02/08/2018
-

Oxford House Community: Meet O
The year has flown by and we are already into the second week of our summer intensive courses. Today we look back at th... Read More
- Blog
-
18/07/2018
-

6 Amazing Events to Make It an
Things are hotting up in Barcelona. There’s so much to see and do during the summer months that it’s hard to know wh... Read More
- Blog
-
03/07/2018
-

How to Improve Your English Ov
The long summer holiday is almost here and we’ve got some top tips on how you can keep up your English over the summer... Read More
- Blog
-
27/06/2018
-

World Cup Vocabulary: Let’s
Football, football, football: the whole world is going crazy for the 2022 FIFA World Cup in Qatar! The beautiful game i... Read More
- Blog
-
20/06/2018
-

The 10 Characteristics Of A �
Learning a second language has a lot in common with learning to play an instrument or sport. They all require frequent p... Read More
- Blog
-
14/06/2018
-
Catch Your Child’s Imaginati
Imagine, for a moment, taking a cooking class in a language you didn’t know - it could be Japanese, Greek, Russian. It... Read More
- Blog
-
06/06/2018
-

Exam Day Tips: The Written Pap
Exams are nerve-wracking. Between going to class, studying at home and worrying about the results, it’s easy to forget... Read More
- Blog
-
31/05/2018
-

10 Reasons to Study English at
Learning a second language, for many people, is one of the best decisions they ever make. Travel, work, culture, educati... Read More
- Blog
-
22/05/2018
-

Shadowing: A New Way to Improv
Speech shadowing is an advanced language learning technique. The idea is simple: you listen to someone speaking and you ... Read More
- Blog
-
09/05/2018
-

The Best Websites to Help Your
Our children learn English at school from a young age - with some even starting basic language classes from as early as ... Read More
- Blog
-
02/05/2018
-

15 Useful English Expressions
When was the last time you painted the town red or saw a flying pig? We wouldn’t be surprised if you are scratchin... Read More
- Blog
-
26/04/2018
-

Help Your Teens Practise Engli
Teenagers today are definitely part of the smartphone generation and many parents are concerned about the amount of time... Read More
- Blog
-
18/04/2018
-

IELTS: Writing Part 1 –
Are you taking an IELTS exam soon? Feeling nervous about the writing paper? Read this article for some top tips and usef... Read More
- Blog
-
13/04/2018
-

Business skills: How to delive
Love them or hate them, at some point we all have to give a business presentation. Occasionally we have to deliver them ... Read More
- Blog
-
04/04/2018
-

10 phrasal verbs to help you b
A lot of students think English is easy to learn - that is until they encounter phrasal verbs! We are sure you have hear... Read More
- Blog
-
29/03/2018
-

6 Unbelievably British Easter
Have you heard of these fascinating British Easter traditions? Great Britain is an ancient island, full of superstition... Read More
- Blog
-
21/03/2018
-

Guide to getting top marks in
Your is coming to an end and exam day is fast approaching. It’s about time to make sure you are prepared for what man... Read More
- Blog
-
14/03/2018
-

4 Ways English Words are Born
Have you ever wondered where English words come from? There are a whopping 171,476 words in the . From aardvark to zyzz... Read More
- Blog
-
07/03/2018
-

Writing an effective essay: Ca
Students take language certifications like the Cambridge B2 First qualification for lots of different reasons. You might... Read More
- Blog
-
28/02/2018
-

5 Powerful Tools to Perfect Yo
Foreign accent and understanding When you meet someone new, what’s the first thing you notice? Is it how they look?... Read More
- Blog
-
22/02/2018
-

Essential Ski Vocabulary [Info
Are you a ski-fanatic that spends all week dreaming about white-capped peaks, fluffy snow and hearty mountain food? ... Read More
- Blog
-
15/02/2018
-
5 Tips to Get the Best Out of
Quizlet, Duolingo, Busuu...there are lots of apps on the market nowadays to help you learn and improve your English. But... Read More
- Blog
-
07/02/2018
-
10 False Friends in English an
Is English really that difficult? English is a Germanic language, which means it has lots of similarities with Germa... Read More
- Blog
-
31/01/2018
-

How to Improve your English wi
If you’ve been studying English for a long time, you’ve probably tried lots of different ways of learning the langua... Read More
- Blog
-
24/01/2018
-

Myths and Mysteries of the Eng
Learning another language as an adult can be frustrating. We’re problem-solvers. We look for patterns in language and ... Read More
- Blog
-
17/01/2018
-

10 Ways to Improve your Englis
Every year is the same. We promise ourselves to eat more healthily, exercise more and save money. It all seems very easy... Read More
- Blog
-
10/01/2018
-

10 English words you need for
Languages are constantly on the move and English is no exception! As technology, culture and politics evolve, we’re fa... Read More
- Blog
-
27/12/2017
-

Catalan Christmas Vs British C
All countries are proud of their quirky traditions and this is no more evident than . In South Africa they eat deep-fri... Read More
- Blog
-
20/12/2017
-

9 Ideas To Kickstart Your Read
You’ve heard about the four skills: reading, writing, and . Some might be more important to you than others. Although... Read More
- Blog
-
13/12/2017
-

How to Write the Perfect Busin
Business is all about communication. Whether it’s colleagues, clients or suppliers, we spend a big chunk of our workin... Read More
- Blog
-
07/12/2017
-

10 Phrasal Verbs You Should Le
Why are phrasal verbs so frustrating? It’s like they’ve been sent from the devil to destroy the morale of English la... Read More
- Blog
-
29/11/2017
-

How to Ace the Cambridge Speak
Exams are terrifying! The big day is here and after all that studying and hard work, it’s finally time to show what y... Read More
- Blog
-
22/11/2017
-

7 Podcasts To Improve Your Lis
Speaking in a foreign language is hard work. Language learners have to think about pronunciation, grammar and vocabulary... Read More
- Blog
-
08/11/2017
-

IELTS: Your Ticket to the Worl
Have you ever thought about dropping everything to go travelling around the world? Today, more and more people are quit... Read More
- Blog
-
01/11/2017
-

6 Language Hacks to Learn Engl
It’s October and you’ve just signed up for an English course. Maybe you want to pass an official exam. Maybe you nee... Read More
- Blog
-
25/10/2017
-

5 Reasons to Learn English in
Learning English is more fun when you do it in a fantastic location like Barcelona. Find out why we think this is the pe... Read More
- Blog
-
18/09/2017
-

FAQ Cambridge courses and Exam
Is it better to do the paper-based or the computer-based exam? We recommend the computer-based exam to our stud... Read More
- Blog
-
11/11/2015
-

Cambridge English Exams or IEL
What exactly is the difference between an IELTS exam and a Cambridge English exam such as the First (FCE) or Advanced (C... Read More
- Blog
-
22/09/2015
CONTACT
Oxford House Language School
C/Diputación 279, Bajos
(entre Pau Claris y Paseo de Gracia).
08007 - Barcelona (Eixample)
Tel: 93 174 00 62 | Fax: 93 488 14 05
info@oxfordhousebcn.com
Oxford TEFL Barcelona
Oxford House Prague
Oxford TEFL Jobs
Legal Notice – Cookie Policy
Ethical channel



Leave a Reply